Abstract: Immunohistochemistry is the basic principle of applied immunology. Antigen-antibody reaction refers to the principle for specific binding between antigens and antibodies. During the process, the chemical reaction makes chromogenic agent (fluorescein, enzyme, metal ion, and isotope) for labelled antibodies highlighted to demonstrate the antigen in tissue cells. It's the qualitative and relative quantitative research for antigen localization.
Keywords: Immunohistochemistry Background Staining, IHC Background Staining, Antigen-antibody Reaction
1. Introduction
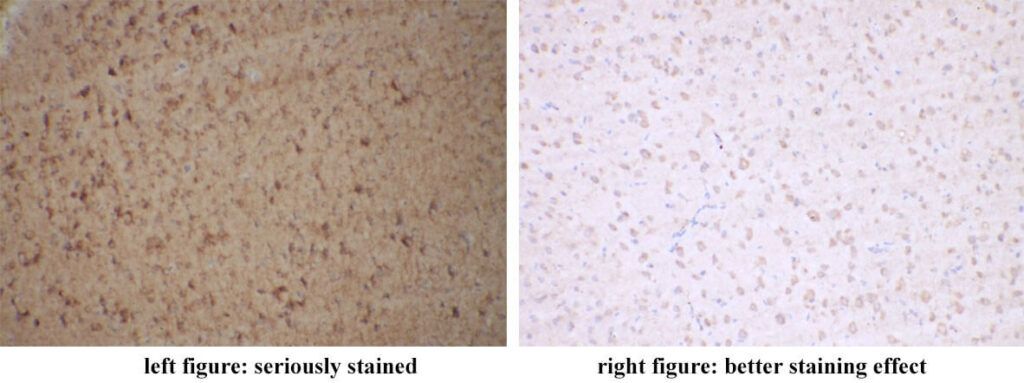
As an analytical approach, non-specific background staining usually exists. Target points in the figure below are membrane localizations. The background of the left figure is seriously stained. The staining effect of the right figure is better.
2. 8 Factors Influencing Immunohistochemistry Background Staining
FineTest has thousands of self-developed antibodies and rich experience in antibody test. Through thousands of slice detections, main factors for non-specific staining are found and summarized.
2.1. Antibody Quality
The low specificity of the antibody target design can result in non-specific staining. Generally, comparing with polyclonal antibodies, the specificity of monoclonal antibodies is higher. Since monoclonal antibodies can identify multiple epitopes on any antigen, monoclonal antibodies can amplify the signal of proteins with low expression level. With higher compatibility for changes in microantigen(organism polymorphism, glycosylation heterogeneity or slight degeneration ), monoclonal antibodies can be applied in detection experiment for target proteins of non-immunogenic species. During the experiment, the selection for suitable antibodies depends on real requirements. Besides, anticorrosion and prevention for repeated freezing should be noted during the storage of antibodies.
2.2. Endogenous Enzymes and Biotins
When liver, kidney or spleen tissues are used as samples, higher level of peroxidases and biotins in those tissues can cause non-specific staining during the experiment for chromogenic system using HRP or biotin-avidin. 0.9% H2O2 can be used to make endogenous peroxidase inactivated. For endogenous biotins, slices should be immersed in 25 μg/mL avidin solution for 15 min before staining. After 15min for PBS cleaning, slices can be stained. 24 mg/mL avidin can be applied to seal slices for 15min as well.
2.3. Higher Antibody Concentration
In order to obtain better chromogenic effect, the used concentration of primary antibodies should be optimized. Instructions from the supplier can be followed. The pretest is necessary to find the best working concentration.
2.4. DAB Staining Time and Deteriorated DAB
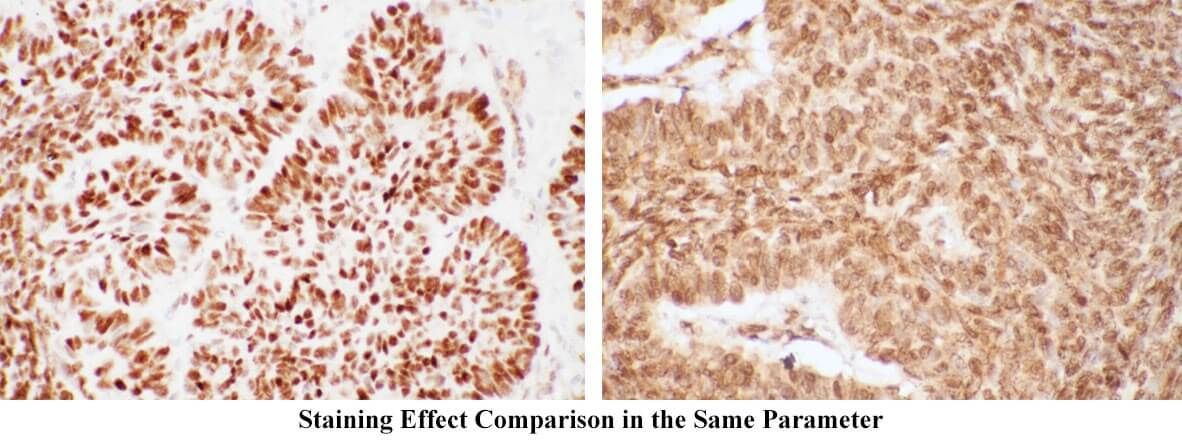
Too long DAB action time can cause background. DAB staining time always changes. During the experiment, timely microscopic examinations should be conducted. When light brown appears, DAB wash should be performed. The too short time of brown shows the antibody concentration is too high. On the contrary, the effect concentration of the antibody is too low. DAB should be stored in dry and dark place. H2O2 is just added before the usage. Immunohistochemistry background staining effects in the same parameter are showed in figures below (left: normal; right: abnormal).
2.5. Dry Tissues
During the experiment process, the surface and surroundings of the sample should be kept wet. The reagent loss for causing background should be avoided. Multiple slices shouldn't be stained at the same time and can be stained in different lots.
2.6. Immersion Time
Slices shouldn't be immersed in buffers or retrieval buffers overnight. The experimental process should be consistent. Influences from unnecessary procedures and unknown factors should be reduced.
2.7. Insufficient Washing
Incubated antibodies should be fully washed. Before using PBS, pH value should be defined. Tween-20 can be added to increase washing strength if necessary.
2.8. Sealing
Serum diluents are used to seal for immunohistochemistry. To remove the non-specific adsorption caused by secondary antibodies, non-immunized animals' serums can be used. E.g. If the secondary antibody is goat anti rabbit, non-immunized goat serum should be chosen. It’s suggested to use PBS to dilute 3-10% solution where slices are incubated for 10-30min under 37°C. It's not necessary to clean after sealing. Moreover, after the tissue is fixed, part free aldehyde group may be residual. The non-specific binding may happen during incubating antibodies. Then, 0.3M glycine can be used to seal.
3. FineTest Antibodies
FineTest offers high-quality validated antibodies, including polyclonal antibodies, monoclonal antibodies, labelled secondary antibodies, internal control/tag antibodies, acetylated/phosphorylated antibodies etc. These antibodies are mainly applied in intracellular and extracellular protein identification, quantitative/positioning research, western blot, immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry, FACS, immunoprecipitation/immunocoprecipitation. FineTest antibodies are strictly tested to ensure the purity and quality. FineTest is always committed to contributing to advance your scientific research.
REFERENCES
An improved protocol of biotinylated tyramine-based immunohistochemistry minimizing nonspecific background staining, PMID: 12502763.
