Abstract: Recombinant protein expression plays an important role in the development of modern biotechnology. Exogenous protein expression via hosts provides a powerful tool for some important protein researches (especially structure and function of human protein). Obtained recombinant proteins must be soluble, stable, correctly folded and active. The solubility of recombinant protein expression is the priority problem. Hence, many fusion tags are introduced. Selection and features of common fusion tags are specified below.
Keywords: Fusion Tag Protein, Recombinant Protein Expression, Protein Research, Fusion Tags for Protein Solubility
1. Features of Common Fusion Tag Protein
1.1. Maltose-binding Protein (MBP)
MBP encoded by malE is a free protein of Escherichia coli K12 family. The molecular weight is 42kDa. The typical feature of MBP tag is the strong solubility. This tag has wide soluble range and high soluble efficiency. MBP tag has wide applications and can specifically bind with amylose. Especially, this tag can be eluted under non-denaturing conditions(10mmol/L maltose) to achieve mono-polarized purification. Besides, MBP fused to c-terminal and n-terminal can contribute to solubility. Currently, commercial MBP fusion tag carriers are available for research needs.
1.2. Glutathione S- transferase (GST)
GST can produce affinity with fixed glutathione. Elution under non-denaturing conditions(10mmol/L reduced glutathione) can contribute to affinity purification. GST can also reduce the degradation to improve the protein stability. However, it's reported that the GST soluble effect is not obvious.
1.3. Thioredoxins
Thioredoxins is a series of oxidoreductase widely present in organisms. It can reduce the binding of disulfide bond via replacing thiodisulfide and usually functions as the Thioredoxins A(TrxA). The molecular weight is 11.6kDa.
1.4. Small ubiquitin-related Modifier(SUMO)
SUMO widely exist in eukaryotes and is not found in prokaryotes. SUMO usually acts as fusion tag and comes from beer yeast. The molecular weight is 11.5kDa.
SUMO can be specifically identified and efficiently degraded by SUMO protease. As a result, the removal process of tag is accurate and efficient. SUMO tag can strength the solubility of recombinant protein and improve the expression level.
Because endogenous SUMO protease are present in eukaryotic cells, wild type SUMO tag can't be applied in eukaryotic expression system. Currently, modified SUMO tag and relevant specific protease has been developed for eukaryotic expression system(e.g. yeast, insect cell, mammalian cell etc.)
1.5. N-utilization substance A(NusA Tag)
NusA protein is a kind of anti-termination factor extending transcription. The molecular weight is about 55kDa.
NusA can promote DNA transcription and slow down bioactivity of translation. Thus, it allows more time for protein folding and help the stable and active recombinant protein expression. The fusion protein still has activity without removing NusA tag.
1.6. Other Fusion Tags
Many fusion tags have their own characteristics and usually are applied in the specific protein fusion expression. E.g. DsbA has high hydrophilicity and can promote soluble protein expression. Besides, DsbA can use the signal peptide to facilitate the transport between cytoplasm and periplasm. This tag is suitable for secretion and expression of protein. ArsC can facilitate soluble expression in E. coli of aggregate exogenous protein.
2. New Advances in Fusion Tags
2.1. Applications of Tandem Tags
TrxA/SUMO/NusA tag can't be applied in affinity purification. Hence, they have to be combined with affinity tags to purify fusion protein. The most common affinity tag is his-tag.
After purification, some recombinant proteins should remove the tag protein to get the target protein. Specific sequence polypeptide added between tag protein and target protein acts as the tag removing recognition site of protease, e.g. enterokinase, Xa factor, TEV and thrombin. After removing tag proteins, amino acid residues remain in N-terminal of target protein. SUMO tag protease can specifically identify the tertiary structure of SUMO. After removing in the Gly-Gly sequence of C-terminal, natural proteins with N segment can be obtained.
Different combined tags can produce different effects. Flexible combination depends on research needs and characteristics of target protein. Utilizing fluorescence characteristics of GFP(green fluorescent protein), some researchers achieve triple tandem among GFP tag, MBP tag and his tag. A new method is employed to express Heparanase I(HepA). The expression method obtains highly purified soluble HepA and monitors the bioactivity during target protein production in real time.
2.2. Soluble Expression of Membrane Protein
Membrane protein exists on the biofilm of lipid and is hydrophobic. Mistakenly expression and folding easily occurs during recombinant expression. Hence, there are many difficulties in recombinant expression of membrane protein. In order to obtain soluble recombinant protein, fusion tag can be fused to membrane protein ready for expression. Studies show tags like MBP, Trx and SUMO can increase the solubility and expression level of membrane protein, especially the membrane protein with small molecular weight (10-20kDa).
2.3. New Derivatives of Common Fusion Tags
Because common fusion tags are limited to more actual applications, current tags can be modified or expressed in other substantial form of tag proteins. Oligomeric GST fusion protein makes purification and elution difficult. Sulfur methylated glutathione can be used to replace glutathione to improve elution effect. MBP belonging to pyrococcus can function as the heat-resisting tag for expressing recombinant protein with thermal stability.
2.4. Discovery for New Fusion Tags
Some new fusion tags are being found and applied. E.g. some fusion proteins can be applied in halophage bacteria and has the potential to be a new fusion tag. Synthesized polypeptide segments can also acts as fusion tag.
3. Tag Selection
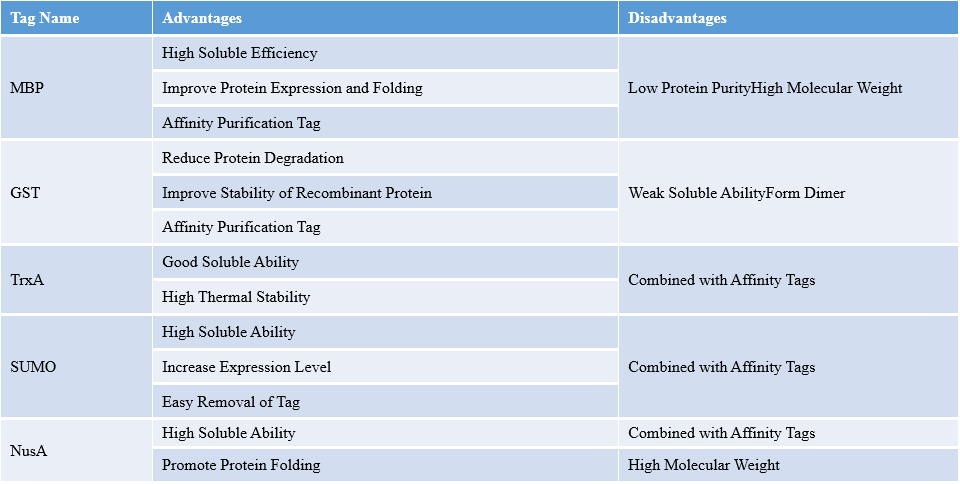
Various factors should be considered during selecting fusion tags. E.g. Can the tag be applied in affinity purification? Is there any influence on spatial structure and bioactivity of target protein, cost and technical method? The rapid selection method is to construct soluble expression vector of various tags. The recombinant protein production depends on the result of expression and purification. Advantages and disadvantages of common fusion tags are specified in the table below.
4. FineTest Recombinant Protein
Browse a list of FineTest recombinant proteins.
