Products
RANKL antibody
Category:
Research Area:
| Synonyms: | CD254 antibody, hRANKL2 antibody, ODF antibody, OPGL antibody, OPTB2 antibody, Osteoprotegerin ligand antibody, RANKL antibody, sOdf antibody, TNFSF11 antibody, TRANCE antibody | ||
| Catalogue No.: | FNab07108 | Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host: | Rabbit | Tested Application: | ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
| Clonality: | polyclonal | Isotype: | IgG |
- SPECIFICATIONS
- Product Name
- RANKL antibody
- Catalogue No.
- FNab07108
- Size
- 100μg
- Form
- liquid
- Purification
- Immunogen affinity purified
- Purity
- ≥95% as determined by SDS-PAGE
- Clonality
- polyclonal
- Isotype
- IgG
- Storage
- PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3, -20℃ for 12 months (Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.)
Immunogen
- Immunogen
- tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 11
- Alternative Names
- CD254 antibody, hRANKL2 antibody, ODF antibody, OPGL antibody, OPTB2 antibody, Osteoprotegerin ligand antibody, RANKL antibody, sOdf antibody, TNFSF11 antibody, TRANCE antibody
- UniProt ID
- O14788
- Observed MW
- 32 kDa
Application
- Tested Applications
- ELISA, WB, IHC, IF
- Recommended dilution
- WB: 1:500 - 1:2000; IHC: 1:50 - 1:200; IF: 1:50 - 1:200
Validated Images
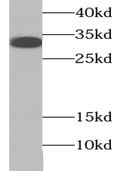 COLO 320 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab07108( RANKL Antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
COLO 320 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab07108( RANKL Antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
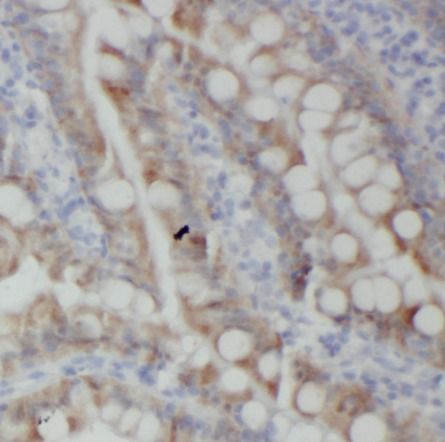 Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human colon tissue slide using FNab07108( RANKL Antibody) at dilution of 1:100
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human colon tissue slide using FNab07108( RANKL Antibody) at dilution of 1:100
- Background
- This gene encodes a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) cytokine family which is a ligand for osteoprotegerin and functions as a key factor for osteoclast differentiation and activation. This protein was shown to be a dentritic cell survival factor and is involved in the regulation of T cell-dependent immune response. T cell activation was reported to induce expression of this gene and lead to an increase of osteoclastogenesis and bone loss. This protein was shown to activate antiapoptotic kinase AKT/PKB through a signaling complex involving SRC kinase and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 6, which indicated this protein may have a role in the regulation of cell apoptosis. Targeted disruption of the related gene in mice led to severe osteopetrosis and a lack of osteoclasts. The deficient mice exhibited defects in early differentiation of T and B lymphocytes, and failed to form lobulo-alveolar mammary structures during pregnancy. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found.



