Products
AKT1 antibody
Category:
Research Area:
| Synonyms: | AKT antibody, AKT1 antibody, PKB antibody, PKB ALPHA antibody, PRKBA antibody, Protein kinase B antibody, Proto oncogene c Akt antibody, RAC antibody, RAC ALPHA antibody, RAC PK alpha antibody | ||
| Catalogue No.: | FNab00268 | Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host: | Rabbit | Tested Application: | ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
| Clonality: | polyclonal | Isotype: | IgG |
- SPECIFICATIONS
- Product Name
- AKT1 antibody
- Catalogue No.
- FNab00268
- Size
- 100μg
- Form
- liquid
- Purification
- Immunogen affinity purified
- Purity
- ≥95% as determined by SDS-PAGE
- Clonality
- polyclonal
- Isotype
- IgG
- Storage
- PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3, -20℃ for 12 months (Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.)
Immunogen
- Immunogen
- v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1
- Alternative Names
- AKT antibody, AKT1 antibody, PKB antibody, PKB ALPHA antibody, PRKBA antibody, Protein kinase B antibody, Proto oncogene c Akt antibody, RAC antibody, RAC ALPHA antibody, RAC PK alpha antibody
- UniProt ID
- P31749
- Observed MW
- 60 kDa
Application
- Tested Applications
- ELISA, WB, IHC, IF
- Recommended dilution
- WB: 1:500 - 1:2000; IHC: 1:50 - 1:100; IF: 1:50 - 1:100
Validated Images
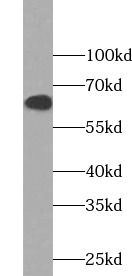 HeLa cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab00268(AKT antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
HeLa cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab00268(AKT antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
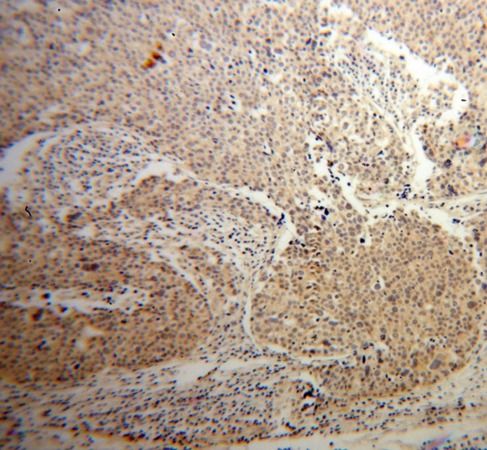 Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human ovary tumor using FNab00268(AKT antibody) at dilution of 1:50
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human ovary tumor using FNab00268(AKT antibody) at dilution of 1:50
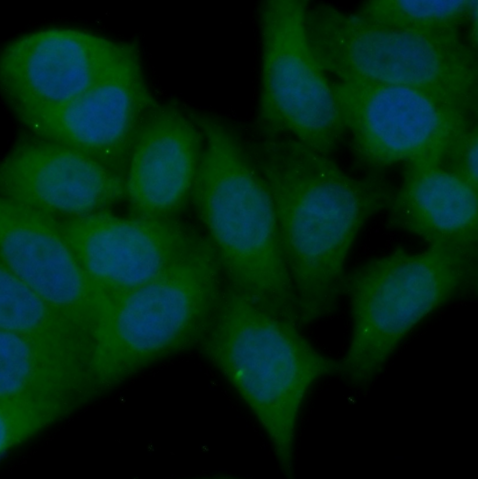 Immunofluorescent analysis of ( 10% Formaldehyde ) fixed HeLa cells using FNab00268( AKT1Antibody) at dilution of 1:50 and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L)
Immunofluorescent analysis of ( 10% Formaldehyde ) fixed HeLa cells using FNab00268( AKT1Antibody) at dilution of 1:50 and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L)
- Background
- The serine-threonine protein kinase encoded by the AKT1 gene is catalytically inactive in serum-starved primary and immortalized fibroblasts. AKT1 and the related AKT2 are activated by platelet-derived growth factor. The activation is rapid and specific, and it is abrogated by mutations in the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT1. It was shown that the activation occurs through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. In the developing nervous system AKT is a critical mediator of growth factor-induced neuronal survival. Survival factors can suppress apoptosis in a transcription-independent manner by activating the serine/threonine kinase AKT1, which then phosphorylates and inactivates components of the apoptotic machinery. Mutations in this gene have been associated with the Proteus syndrome. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene.



